An introduction to MUDROD recommendation algorithm
Posted 2018-04-23 by Lewis John McGibbney
With the recent advances in remote sensing satellites and other sensors, geographic datasets have been growing faster than ever. In response, a number of Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) components (e.g. catalogues and portals) have been developed to archive and made those datasets available online. However, finding the right data for scientific research and application development is still a challenge due to the lack of data relevancy information.
Recommendation has become extremely common in recent years and are utilized in a variety of areas to help users quickly find useful information. We propose a recommendation system to improve geographic data discovery by mining and utilizing metadata and usage logs. Metadata abstracts are processed with natural language processing methods to find semantic relationship between metadata. Metadata variables are used to calculate spatial and temporal similarity between metadata. In addition, portal logs are analysed to introduce user preference.
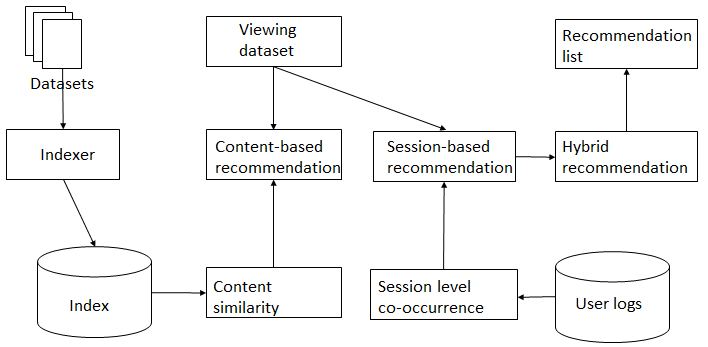 Figure 1. Recommendation workflow
Figure 1. Recommendation workflow
The system starts by pre-processing raw web logs and metadata (Figure 1). After pre-processing step, sessions are reconstructed from raw web logs and then used to calculate session-based metadata similarity. Metadata are harvested from PO.DAAC web service APIs. Metadata variable values are then converted to value using the united unit to calculate metadata content similarity. Elasticsearch is used to store all of the above similarities. Once a user views a metadata record, the system finds the top-k related metadata with a hybrid recommendation methodology. The hybrid recommendation module integrates results from content-based recommendation and session-based recommendation methods and ranks the final recommendation list in a descending order of similarity.
